NOTICE

If the operand value for a type conversion operator is outside of the value range
of the target data type, then the result output depends on the processor type and
is therefore undefined. This is the case, for example, when a negative operand value
is converted from LREAL to the target data type UINT.
Information can be lost when converting from larger data types to smaller data types.




NOTICE

If the floating-point number is within the value range of the target data type, then the conversion operates the same way on all systems.




NOTICE

If the floating-point number to be converted exceeds the range limit, then the first bytes of the number are ignored.
The operators convert a floating-point number into the specified data types and return a type-converted value. If applicable, the conversion is rounded.
Call
Syntax
<variable name> := <floating-point conversion operator> ( <floating-point operand> ); <floating-point operand> = <variable name> | <literal> <floating-point type> = REAL | LREAL
Operators
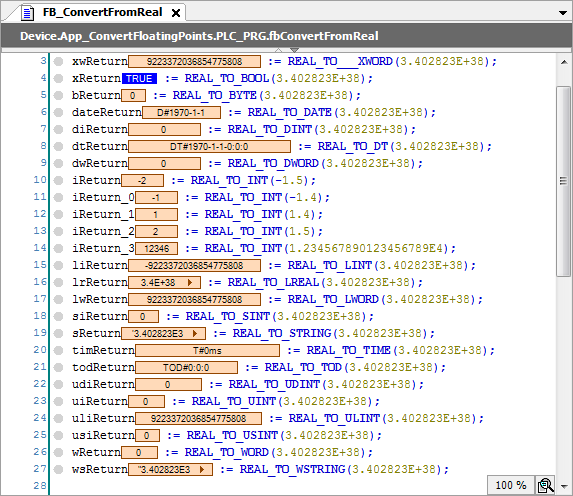
REAL_TO___UXINT REAL_TO___XINT REAL_TO___XWORD REAL_TO_BIT REAL_TO_BOOL REAL_TO_BYTE REAL_TO_DATE REAL_TO_DINT REAL_TO_DT REAL_TO_DWORD REAL_TO_INT REAL_TO_LINT REAL_TO_LREAL REAL_TO_LTIME REAL_TO_LWORD REAL_TO_SINT REAL_TO_STRING REAL_TO_TIME REAL_TO_TOD REAL_TO_UDINT REAL_TO_UINT REAL_TO_ULINT REAL_TO_USINT REAL_TO_WORD REAL_TO_WSTRING LREAL_TO___UXINT LREAL_TO___XINT LREAL_TO___XWORD LREAL_TO_BIT LREAL_TO_BOOL LREAL_TO_BYTE LREAL_TO_DATE LREAL_TO_DINT LREAL_TO_DT LREAL_TO_DWORD LREAL_TO_INT LREAL_TO_LINT LREAL_TO_LTIME LREAL_TO_LWORD LREAL_TO_REAL LREAL_TO_SINT LREAL_TO_STRING LREAL_TO_TIME LREAL_TO_TOD LREAL_TO_UDINT LREAL_TO_UINT LREAL_TO_ULINT LREAL_TO_USINT LREAL_TO_WORD LREAL_TO_WSTRING
Rounding
When converting to an integer, the operand is rounded up or down to an integer value. For 1 to 4 after the decimal point, the number is rounded down. For 5 to 9, the number is rounded up. Then the rounded number is converted to the specified integer type. If the rounded value is outside of the integer value range, then an undefined, target system-dependent value is returned. An exception error is also possible then.




NOTICE

The rounding logic for borderline cases depends on the target system or the FPU (Floating
Point Unit) of the target system. For example, a value of -1.5 can be converted differently on different controllers.
To program target system-independent code, you have to catch value range overflows across the application.
Converting to a string




NOTICE

String manipulation when converting to STRING or WSTRING
When converting the type to STRING or WSTRING, the typed value is left-aligned as a character string and truncated if it is too
long. Therefore, declare the return variable for the type conversion operators <>_TO_STRING and <>_TO_WSTRING long enough that the character string has enough space without any manipulation.
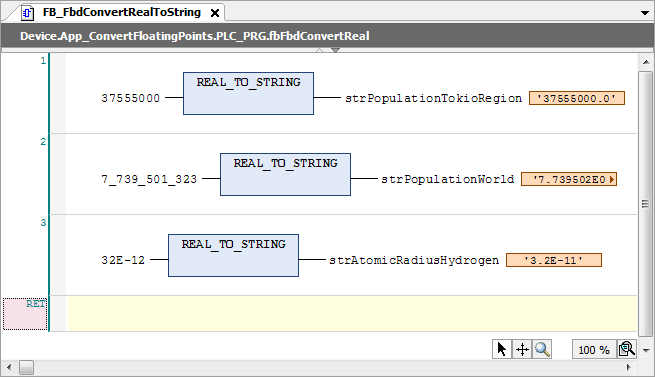
For a floating-point number conversion to a string, the number of decimal places of
the mantissa is limited to 6. If the number is < 1, then the mantissa is 1 <= m < 10. If the mantissa has more digits after the comma, then it is rounded to the 6th digit
and then converted.
The string variable may also be declared too short for the return value. In this case, the return string is truncated on the right.
Examples
ST implementation language