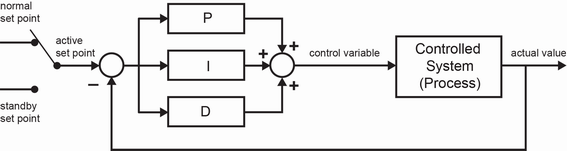
A proportional-integral-derivative controller (PID controller) is a closed-loop control method, widely used in industrial control systems. A PID controller manipulates a control variable to minimize the error between process actual value and a desired process set point.
The PID controller algorithm involves three parameters: The proportional, the integral and derivative values, abbreviated as P, I, and D.
In the Temperature Control library package in AC500 V3, a PID controller with the first order delay T1 is used to prevent spike of derivative part D. In the world of temperature control, set point is the desired temperature of the process, actual value is the actual temperature, and control variable is the PWM signal for controlling the heater and cooler.