For a detailed description of the mounting, disassembly and connection of the module, please refer to the ⮫ installation instructions.
The modules are plugged on an I/O terminal unit.
Properly position the modules and press until they lock in place. The terminal units are mounted on a DIN rail or with 2 screws plus the additional accessory for wall mounting.
⮫ “TA526 - Wall mounting accessory”
The connection of the I/O channels is carried out using the 40 terminals of the I/O terminal unit. I/O modules can be replaced without re-wiring the terminal units.
The terminals 1.8, 2.8, 3.8, 4.8, 1.9, 2.9, 3.9 and 4.9 are electrically interconnected within the I/O terminal units and always have the same assignment, independent of the inserted module:
Terminals 1.8, 2.8, 3.8 and 4.8: process voltage UP = +24 V DC
Terminals 1.9, 2.9, 3.9 and 4.9: process voltage ZP = 0 V
|
Terminals |
Signal |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
2.0, 2.2, 2.4, 2.6 |
I0+ ... I3+ |
Positive poles of the first 4 analog inputs |
|
1.0, 1.2, 1.4, 1.6 |
I0- ... I3- |
Negative poles of the first 4 analog inputs |
|
2.1, 2.3, 2.5, 2.7 |
I0A ... I3A |
Connections A (supply) of the first 4 analog inputs |
|
1.1, 1.3, 1.5, 1.7 |
I0B ... I3B |
Connections B (analog ground) of the first 4 analog inputs |
|
4.0, 4.2, 4.4, 4.6 |
I4+ ... I7+ |
Positive poles of the following 4 analog inputs |
|
3.0, 3.2, 3.4, 3.6 |
I4- ... I7- |
Negative poles of the following 4 analog inputs |
|
4.1, 4.3, 4.5, 4.7 |
I4A ... I7A |
Connections A (supply) of the following 4 analog inputs |
|
3.1, 3.3, 3.5, 3.7 |
I4B ... I7B |
Connections B (analog ground) of the following 4 analog inputs |




CAUTION

Analog sensors must be galvanically isolated against the ground. In order to avoid inaccuracy with the measuring results, the analog sensors should also be isolated against the power supply.




CAUTION

There is no galvanic isolation between the analog circuitry and ZP/UP. Therefore, the analog sensors must be galvanically isolated in order to avoid loops via the ground potential or the supply voltage.
The "IxB" clamps (x=0 ... 7) of the analog inputs are galvanically connected to each other. They form an "Analog Ground Signal" (AGND) for the module.
The negative poles of the analog inputs Ix- may accept a potential difference up to ±20 V DC with regard to the common reference potential IxB (AGND, ZP). Observing this maximum voltage difference, analog current inputs of one module can be switched in series to each other and also with current inputs of other modules.
For the open-circuit detection (wire break), each positive analog input channel Ix+ is pulled up to "plus" by a high-resistance resistor and each negative analog input channel Ix- is pulled down to "minus" by a resistor. If wire break occurs, a maximum voltage (overflow or underflow) will be read in then.
The internal power supply voltage for the module's circuitry is carried out via the I/O bus (provided by a communication interface module or a CPU). Thus, the current consumption from 24 V DC power supply at the terminals L+/UP and M/ZP of the CPU/communication interface module increases by 2 mA per AI531.
The external power supply connection is carried out via the UP (+24 V DC) and the ZP (0 V DC) terminals.




WARNING

Removal/Insertion under power
Removal or insertion under power is permissible only if all conditions for hot swapping are fullfilled.
⮫ “Replace an I/O module with hot swap”
The devices are not designed for removal or insertion under power when the conditions for hot swap do not apply. Because of unforeseeable consequences, it is not allowed to plug in or unplug devices with the power being ON.
Make sure that all voltage sources (supply and process voltage) are switched off before doing any of the following actions:
-
Connect or disconnect any signal or terminal block.
-
Remove, mount or replace a module.
Disconnecting any powered devices while they are energized in a hazardous location could result in an electric arc, which could create an ignition source resulting in fire or explosion.
Prior to proceeding, make sure that power is been disconnected and that the area has been thoroughly checked to ensure that flammable materials are not present.
The devices must not be opened when in operation. The same applies to the network interfaces.




NOTICE

Risk of damaging the PLC modules!
Overvoltages and short circuits might damage the PLC modules.
-
Make sure that all voltage sources (supply voltage and process supply voltage) are switched off before you begin with operations on the system.
-
Never connect any voltages or signals to reserved terminals (marked with ---). Reserved terminals may carry internal voltages.
Generally, analog signals must be laid in shielded cables. The cable shields must be grounded at both sides of the cables. In order to avoid unacceptable potential differences between different parts of the installation, low resistance equipotential bonding conductors must be laid.
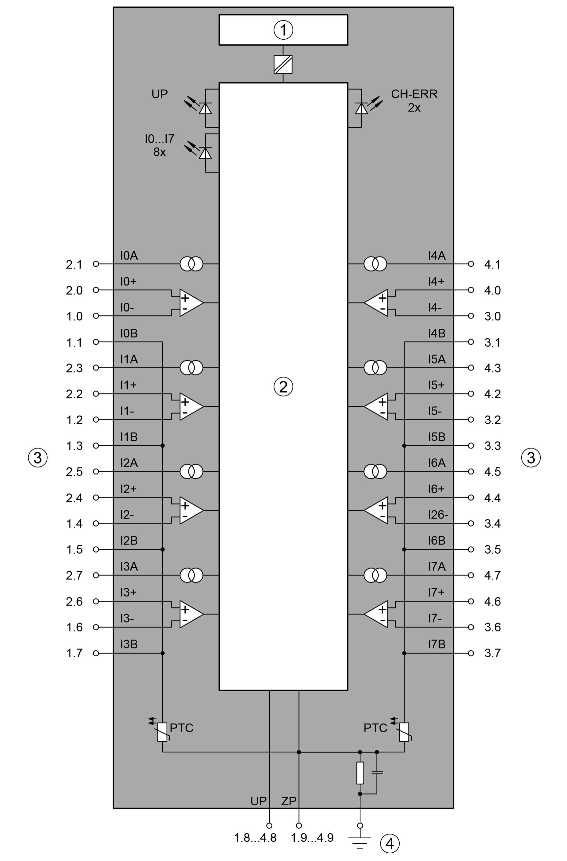
- 1
-
I/O bus interface
- 2
-
Logic
- 3
-
Analog inputs
- 4
-
Functional earth connection




CAUTION

By installing equipotential bonding conductors between the different parts of the system, it must be ensured that the potential difference between ZP and AGND never can exceed 1 V.




CAUTION

The process supply voltage must be included in the grounding concept (e. g. grounding of the negative terminal).
The module provides several diagnosis functions.
-
Connection of active-type analog sensors (Voltage) with galvanically isolated power supply
-
Connection of active-type analog sensors (Voltage) with no galvanically isolated power supply
-
Connection of active-type analog sensors (Current) with galvanically isolated power supply
-
Connection of active-type analog sensors (Current) with galvanically isolated power supply and series-connection of an additional input
-
Connection of passive-type analog sensors (Current)
-
Connection of passive-type analog sensors (Current) and series-connection of an additional analog sensor
-
Connection of digital signal sources at analog inputs
-
Connection of resistance thermometers in 2-wire configuration
-
Connection of resistance thermometers in 3-wire configuration
-
Connection of resistance thermometers in 4-wire configuration
-
Connection of resistors in 2-wire configuration
-
Connection of a resistance measuring bridge with internal supply
-
Connection of a resistance measuring bridge with external supply
-
Connection of thermocouples





