Symbol:

Category: “Date/Time Controls”
The element is a clock that displays the current time of day. The clock can also display a random time.
Element properties
|
“Element name” |
Example: |
|
“Type of element” |
“Analog Clock” |
Element property 'Position'
The position defines the location and size of the element in the visualization window. These are based on the Cartesian coordinate system. The origin is located at the upper left corner of the window. The positive horizontal x-axis runs to the right. The positive vertical y-axis runs downwards.
|
“X” |
X coordinate of the upper left corner of the element Specified in pixels. Example: |
|
“Y” |
Y coordinate of the upper left corner of the element Specified in pixels. Example: |
|
“Width” |
Specified in pixels. Example: |
|
“Height” |
Specified in pixels. Example: |
You can also change the values by dragging the box symbols ( ) to other positions in the editor.
) to other positions in the editor.
Element property 'Center'
The properties contain fixed values for the coordinates of the point of rotation.
This point of rotation is shown as the  symbol. The point is used as the center for rotating and scaling.
symbol. The point is used as the center for rotating and scaling.
|
“X” |
X-coordinate of the point of rotation |
|
“Y” |
Y-coordinate of the point of rotation |
You can also change the values by dragging the symbols ( ) to other positions in the editor.
) to other positions in the editor.
Element property 'Time Display'
|
“Use system time” |
|
|
“Variable” |
Variable (time data type Example: Requirement: The “Use system time” property is not activated. |
See also
|
“Design” |
|
Element property 'Absolute movement'
The properties contain IEC variables for controlling the position of the element dynamically. The reference point is the upper left corner of the element. In runtime mode, the entire element is moved.
|
“Movement” |
||
|
“X” |
Variable (numeric data type). Defines the X position (in pixels). Example: Increasing this value in runtime mode moves the element to the right. |
|
|
“Y” |
Variable (numeric data type). Defines the Y position (in pixels). Example: Increasing this value in runtime mode moves the element downwards. |
|
|
“Rotation” |
Variable (numeric data type). Defines the angle of rotation (in degrees). Example: The midpoint of the element rotates at the “Center” point. This rotation point is shown as the In runtime mode, the alignment of the element remains the same with respect to the coordinate system of the visualization. Increasing the value rotates the element to the right. |
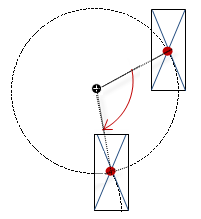 |
|
“Scaling” |
Variable (integer data type). Causes centric stretching. Example: The reference point is the “Center” property. The value |
|
|
“Interior rotation” |
Variable (numeric data type). Defines the angle of rotation (in degrees). Example: In runtime mode, the element rotates about the point of rotation specified in “Center” according to the value of the variable. In addition, the alignment of the element rotates according to the coordinate system of the visualization. Increasing the value in the code rotates clockwise. The rotation point is shown as the Note: If a static angle of rotation is specified in the property “Position Angle”, then the static angle of rotation is added to the variable angle of rotation (offset) when the visualization is executed. |
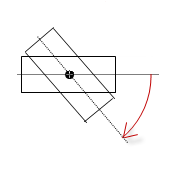 |
|
“Use REAL values” |
Note: Only available if the device supports the use of REAL coordinates.
The option allows for the individual fine-tuning of drawing the element, for example for the visualization of a smoother rotation. Hint: If a horizontal or vertical line is drawn blurry on a specific visualization platform, then this can be corrected by an offset of 0.5px in the direction of the line thickness. |
|
You can link the variables to a unit conversion.
The properties “X”, “Y”, “Rotation”, and “Interior rotation” are supported by the "Client Animation" functionality.
See also
Element property 'Settings'
Requirement: The “Property” is “Explicit”. Only then is the “Clock Settings” category visible.
|
“Background color” |
Color variants of the default background image
|
|
“Own background” |
Background display with the specific “Image”. Replaces the default background image. |
|
“Image” |
Image from an image pool or library Example: |
|
“Transparency color” |
The transparent color in the image representation. Example: “White”. The white parts of the image are transparent. |
|
“Use background color” |
Requirement: No image reference is given in the “Image” property. |
|
“Background color” |
Style color or color Requirement: “Use background color” is activated. |
|
“Hand style” |
Example: “Thin arrow” |
|
“Color hour hand” |
Style color or color for the hands |
|
“Color minute hand” |
|
|
“Color second hand” |
|
“Lines style” |
Clock face graduation
|
|
“Color” |
Color of the clock face graduation |
|
“Line width” |
Line weight of the clock face graduation |
|
“Scale in 3D” |
|
|
“Style of numerics” |
Digits on the clock face
|
|
“Font” |
Font for displaying the digits |
|
“Font color” |
Font for displaying the digits |
|
“Color” |
Color of the center of the clock |
|
“Usage of” |
|
|
“Positioning” |
Requirement: Visible when the “Usage or” property is set to “Individual settings”. |
|
“Numerics movement” |
Value (in pixels) for shifting the digits. Example: |
|
“Line movement” |
Value (in pixels) for shifting the hour lines. Example: |
|
“Hands scaling” |
Factor for scaling the length of the hour hand. You can customize the exact position of the hour hand relative to the background image. Example: |
|
“Scaling type” |
Defines the scaling of the height and width of the element.
|
|
“Optimized drawing” |
Hint: Disable this option only for extreme exceptions. |
Element property 'Absolute movement'
The properties contain IEC variables for controlling the position of the element dynamically. The reference point is the upper left corner of the element. In runtime mode, the entire element is moved.
|
“Movement” |
||
|
“X” |
Variable (numeric data type). Defines the X position (in pixels). Example: Increasing this value in runtime mode moves the element to the right. |
|
|
“Y” |
Variable (numeric data type). Defines the Y position (in pixels). Example: Increasing this value in runtime mode moves the element downwards. |
|
|
“Rotation” |
Variable (numeric data type). Defines the angle of rotation (in degrees). Example: The midpoint of the element rotates at the “Center” point. This rotation point is shown as the In runtime mode, the alignment of the element remains the same with respect to the coordinate system of the visualization. Increasing the value rotates the element to the right. |
 |
|
“Interior rotation” |
Variable (numeric data type). Defines the angle of rotation (in degrees). Example: In runtime mode, the element rotates about the point of rotation specified in “Center” according to the value of the variable. In addition, the alignment of the element rotates according to the coordinate system of the visualization. Increasing the value in the code rotates clockwise. The rotation point is shown as the Note: If a static angle of rotation is specified in the “Position Angle” property, then the static angle of rotation is added to the variable angle of rotation (offset) when the visualization is executed. |
 |
You can link the variables to a unit conversion.
The “X”, “Y”, “Rotation”, and “Interior rotation” properties are supported by the "Client Animation" functionality.
See also
Element property 'State variables'
The variables control the element behavior dynamically.
|
“Invisible” |
Variable (
|
The “Invisible” property is supported by the "Client Animation" functionality.
These properties are available only when you have selected the “Support client animations and overlay of native elements” option in the Visualization Manager.
|
“Animation duration” |
Defines the duration (in milliseconds) in which the element runs an animation
Animatable properties
The animated movement is executed when at least one value of an animatable property has changed. The movement then executed is not jerky, but is smooth within the specified animation duration. The visualization element travels to the specified position while rotating dynamically. The transitions are smooth. |
|
“Move to foreground” |
Moves the visualization element to the foreground Variable ( Example:
|







 : The system time of the PLC is displayed.
: The system time of the PLC is displayed. : The background image is redrawn in cycles.
: The background image is redrawn in cycles.