Symbol:

Category: “Alarm Manager”
The element displays alarms in a list. In the element properties, you specify which information is shown. You define the appearance of the element and the variables that control the element behavior.
In online mode, you can sort an alarm table by a specific column – even in the classic view. Click into the column header. A small triangle indicates the current sort order (ascending, descending). Clicking the symbol reverses the order.
Sorting inside the column depends on the type of the contained information. The "Priority" column is sorted numerically, and the "Message" and "Class" columns alphabetically. The "Value" and "Latch" columns may contain different value types. In this case, sorting is first by type (blank, Boolean, numeric value, character string) and then either numerically or alphabetically depending on the type.
If an alarm history has been created, then you can programmatically delete it at runtime. The recording starts again from the time of deletion. See the help page for "Visualizing Alarm Management".
Element properties
|
“Element name” |
Example: |
|
“Type of element” |
“Alarm Table” |
|
“Data source” |
Selection of the device and the application where the data to be visualized and the alarms are generated
|
See also
Element property 'Alarm configuration'
|
“Alarm groups” |
Opens the “Select Alarm Group” dialog where you define the alarm groups that you want to display. |
|
“Priority from” |
Least priority for alarm display. (0 to 255). |
|
“Priority to” |
Greatest priority for alarm display. (0 to 255). |
|
“Alarm classes” |
Opens the “Select Class Group” dialog where you define the alarm classes that you want to display. |
|
“Filter criterion” |
For the “Alarm Banner” element only
|
|
“Filter by latch 1” |
The generated alarms (previous and current) can be filtered by the contents of “Latch variable 1”, which is specified in the configuration of the alarm group. In “Filter type”, you define whether or not the filtering is performed by a string value or a numerical value.
|
|
“Filter by time range” |
The generated alarms (remote, historical, local) can be displayed for a specified time range. You use the “Filter type” to define whether filtering by time range is enabled or disabled.
|
Element property 'General table configuration'
|
“Show row header” |
|
|
“Show column header” |
|
|
“Row height” |
Height of the table rows (in pixels). |
|
“Row header width” |
Width of the line header (in pixels). |
|
“Scrollbar size” |
Width of the scrollbar when it runs vertically. Width of the scrollbar when it runs horizontally. Specified in pixels |
|
“Automatic line break for alarm message” |
|
Element property 'Columns: Column [<n>]'
By default, columns [0] and [1] are configured: “Time stamp” and “Message text”. You can create more columns by clicking the “Create new”, and remove columns by clicking “Delete”.
Animations (dynamic text, font variables), text, and tooltip are not supported.
|
“Column header” |
The standard header is set and changed here by specifying a new text. |
|
“Use text alignment in title” |
|
|
“Width” |
Width of the column (in pixels). |
|
“Data type” |
Notice about time stamps: For use in a TargetVisu or WebVisu, you can control the
date and time format with the help of the global string variables from the library
Define the information to be displayed in the column.
|
|
“Text alignment” |
Alignment of the text in this column
|
|
“Color settings” |
|
See also
Element property 'Position'
The position defines the location and size of the element in the visualization window. These are based on the Cartesian coordinate system. The origin is located at the upper left corner of the window. The positive horizontal x-axis runs to the right. The positive vertical y-axis runs downwards.
|
“X” |
X coordinate of the upper left corner of the element Specified in pixels. Example: |
|
“Y” |
Y coordinate of the upper left corner of the element Specified in pixels. Example: |
|
“Width” |
Specified in pixels. Example: |
|
“Height” |
Specified in pixels. Example: |
You can also change the values by dragging the box symbols ( ) to other positions in the editor.
) to other positions in the editor.
Element property 'Center'
The properties contain fixed values for the coordinates of the point of rotation.
This point of rotation is shown as the  symbol. The point is used as the center for rotating and scaling.
symbol. The point is used as the center for rotating and scaling.
|
“X” |
X-coordinate of the point of rotation |
|
“Y” |
Y-coordinate of the point of rotation |
You can also change the values by dragging the symbols ( ) to other positions in the editor.
) to other positions in the editor.
Element property 'Text properties'
The properties contain fixed values for the text properties.
|
“Font” |
Example: “Default”
|
|
“Font color” |
Example: “Black”
|
|
“Transparency” |
Whole number (value range from Example:
Please note: If the color is a style color and already has a transparency value, then this property is write-protected. |
Element property 'Selection'
|
“Selection color” |
Fill color of the selected row |
|
“Selection font color” |
Font color of the selected row |
|
“Frame around selected cells” |
|
|
“Variable for selected alarm group” |
Name of the affected alarm group; type: |
|
“Variable for selected alarm ID” |
Alarm ID of the affected alarm group; type: |
|
“Variable for selected line” |
Index of the selected alarm line (0-based). The index can be read and written; integer data type |
|
“Variable for valid selection” |
TRUE: An alarm line is selected. FALSE: The selection is invalid. For example, for an empty alarm table or when an alarm is not selected yet. |
|
“Variable for selected alarm information” |
Information about the selected alarm. Type For easy usage, the function block Example: The following information is available:
|
Element property 'Control variables'
Boolean variables are defined here for executing specific actions in the table can be executed at runtime.
|
“Acknowledge selected” |
Variable ( Example: If the assigned variable is |
|
“Acknowledge all visible” |
Variable ( Example: If the assigned variable is |
|
“History” |
Variable ( Example: If the assigned variable is Note: Acknowledgment is not possible in this view. |
|
“Freeze scroll position” |
Variable ( Example: If the assigned variable is |
|
“Count alarms” |
Variable (integer data type) Example: Number of alarms that are currently displayed in the alarm table. Defined by the alarm table. |
|
“Count visible rows” |
Variable (integer data type) Example: Number of alarms that can be displayed on one page of the alarm table. Defined by the alarm table. |
|
“Current scroll index” |
Variable (integer data type) Example: The index of the first visible row if the alarm table (0-based). The variable can be read and written. |
|
“Current column sorting” |
Variable (integer data type) Example: The variable contains a value of the enumeration "VisuElemsAlarm.VisuEnumAlarmDataType". This value determines the column that sorts the alarm table. |
|
“Variable for sorting direction” |
Variable (BOOL) Example: The variable determines the sort order for the entries in the alarm table ( |
You can also use the “Insert Elements for Acknowledging Alarms” command to define buttons with predefined control variables.
Element property 'Absolute movement'
The properties contain IEC variables for controlling the position of the element dynamically. The reference point is the upper left corner of the element. In runtime mode, the entire element is moved.
|
“Movement” |
||
|
“X” |
Variable (numeric data type). Defines the X position (in pixels). Example: Increasing this value in runtime mode moves the element to the right. |
|
|
“Y” |
Variable (numeric data type). Defines the Y position (in pixels). Example: Increasing this value in runtime mode moves the element downwards. |
|
|
“Rotation” |
Variable (numeric data type). Defines the angle of rotation (in degrees). Example: The midpoint of the element rotates at the “Center” point. This rotation point is shown as the In runtime mode, the alignment of the element remains the same with respect to the coordinate system of the visualization. Increasing the value rotates the element to the right. |
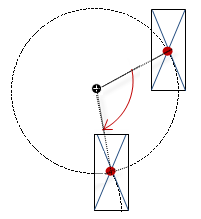 |
|
“Interior rotation” |
Variable (numeric data type). Defines the angle of rotation (in degrees). Example: In runtime mode, the element rotates about the point of rotation specified in “Center” according to the value of the variable. In addition, the alignment of the element rotates according to the coordinate system of the visualization. Increasing the value in the code rotates clockwise. The rotation point is shown as the Note: If a static angle of rotation is specified in the “Position Angle” property, then the static angle of rotation is added to the variable angle of rotation (offset) when the visualization is executed. |
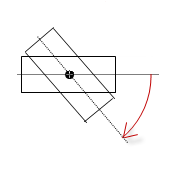 |
You can link the variables to a unit conversion.
The “X”, “Y”, “Rotation”, and “Interior rotation” properties are supported by the "Client Animation" functionality.
See also
Element property 'State variables'
The variables control the element behavior dynamically.
|
“Invisible” |
Variable (
|
The “Invisible” property is supported by the "Client Animation" functionality.
These properties are available only when you have selected the “Support client animations and overlay of native elements” option in the Visualization Manager.
|
“Animation duration” |
Defines the duration (in milliseconds) in which the element runs an animation
Animatable properties
The animated movement is executed when at least one value of an animatable property has changed. The movement then executed is not jerky, but is smooth within the specified animation duration. The visualization element travels to the specified position while rotating dynamically. The transitions are smooth. |
|
“Move to foreground” |
Moves the visualization element to the foreground Variable ( Example:
|
Element property 'Access rights'
Requirement: User management is set up for the visualization.
|
“Access rights” |
Opens the “Access rights” dialog. There you can edit the access privileges for the element. Status messages:
|
See also









 : Display of the row number at the beginning of the row.
: Display of the row number at the beginning of the row. : The message text is truncated at the end of the column, if the text is too long.
: The message text is truncated at the end of the column, if the text is too long. : The
: The  : Drop-down list with style fonts.
: Drop-down list with style fonts.