BACnet can run on different local area network types. The AC500 B-BC supports the following ones:
-
MS/TP (Master Slave / Token Passing), based on serial RS-485
-
BACnet IP, based on Ethernet / UDP / IP
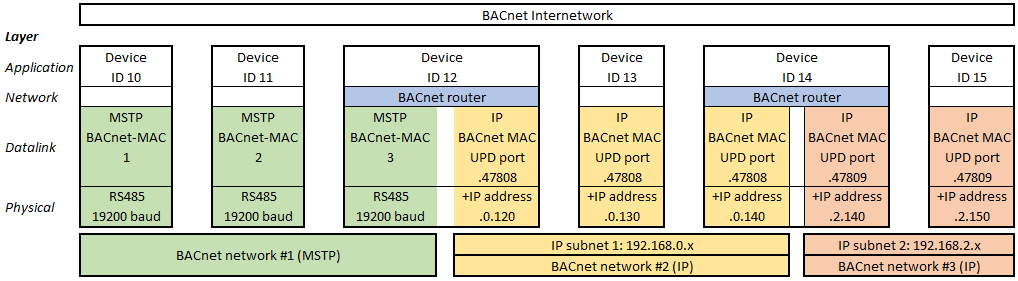
Different networks can be combined to one common “BACnet internetwork”. The figure above shows an example of some BACnet devices in one “BACnet internetwork”. Each device has a device ID (10 to 15) which must be unique on application level. Services on application level (e.g. read or write request) are working with these device IDs and need no addressing information of the lower levels.
The example “BACnet internetwork” consists of different BACnet networks:
-
BACnet MS/TP network connecting device 10, 11 and 12
-
BACnet IP network (UDP port 47808), consisting of one IP subnets with IP range 192.168.0.x, connecting device 12, 13 and 14
-
BACnet IP network (UDP port 47809), consisting of one IP subnet with IP range 192.168.2.x, connecting device 14 and 15
Addressing in a BACnet network is done through datalinks which must have a unique BACnet MAC address (which is different to an Ethernet MAC address).
-
In a MS/TP network the BACnet MAC address is just one octet (1, 2, 3 in the example).
-
In an IP network the BACnet MAC address is the combination of the IP address and the UDP port number (for example 192.168.0.130.47808 for device 13). The following 16 UDP ports are reserved for BACnet: BAC0 (=47808 decimal) to BACF.
To form a common “BACnet internetwork” the single BACnet networks must be combined by BACnet routers. AC500 can act as a BACnet router between BACnet MS/TP and IP networks (device 12 in the figure above) or between two different BACnet IP networks (device 14).
Two IP subnets using the same UDP ports can be combined to one BACnet IP network with an internet router.
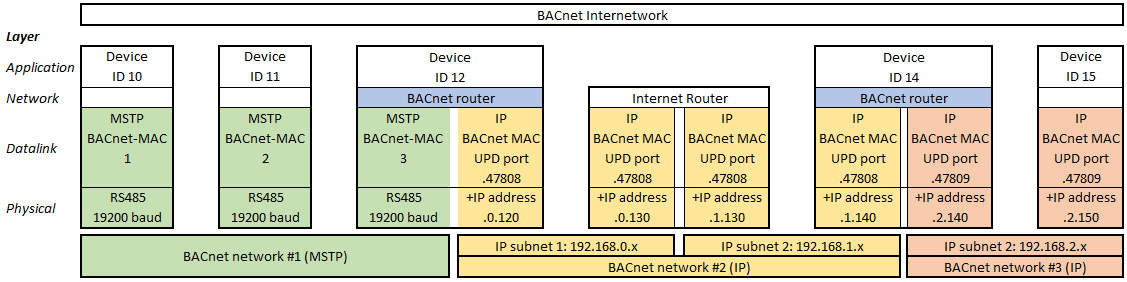
The problem is that internet routers block local broadcast messages, which are required for BACnet communication. This can be solved by “Broadcast Management Devices” (BBDM). The PLC can be configured as BBDM. In the figure above the devices 12 and 14 should be configured as BBDM in order to enable the BACnet communication across the internet router.
An alternative is to configure the PLC as foreign BACnet device if an IP subnet contains no BBDM device to pass broadcast messages over internet routers.
Configuring the AC500 as BBDM or foreign device is described in ⮫ “Configuration of datalinks ”.






