The “Mapping” and “Control Type” tab can be selected if the user wants to set a “Control type” other than CSP (default) and mappings other than default (Control Word, Set Position, Status Word, Actual Position). It can be found under the axis object here:
Control type
By default, wizard is selected for “Cyclic synchronous position mode (CSP)”. User can change the same based on the application requirement. The supported control modes are:
Cyclic synchronous position mode (CSP).
Cyclic synchronous velocity mode (CSV).
Cyclic synchronous velocity mode for load control (CSVL).
Cyclic synchronous torque mode (Limited CST).
CSVL is an ABB specific mode to achieve load control/profiling. By using this mode, the user can use the “Motion Control Load library” which is implemented based on the “PLCopen Motion Part 6 – Fluid Power Extensions”. For more details on load/torque control please refer to the library integrated documentation, system technology in online help file and the example program / description from example program folder.
Additional PDO mapping
If the application needs “Additional PDO mapping” the wizard helps the user to add most used PDO mapping just by selecting them here.
Based on the control type selected, a few of the mandatory PDO mapping are generated automatically and from additional mapping area in wizard user can find the most common PDO mapping and user can add the same based on the application requirement.
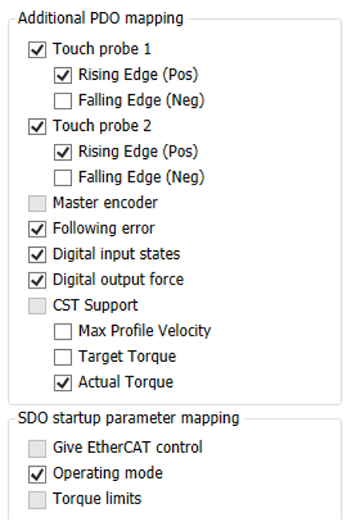
The user can add additional PDO mapping which are not listed here manually by enabling the expert settings from the slave device general configuration page (as described earlier).
SDO start-up parameter mapping
By default, two of the SDO startup parameters are selected and it is recommended not to change these unless the user has expert level knowledge of DS 402 control modes or intends to do non-standard start up coding as it will change the expected operation of the axis at start up.

The user can select the “Torque limits” and the torque values set from the “Settings” page will be written to the respective slave drives startup parameters list.

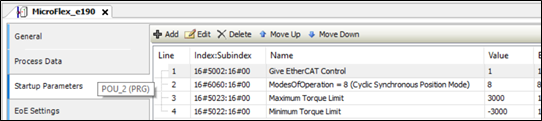
Once these settings are made and the generated code is executed you can see that these settings have change the drives EtherCAT slave configuration as shown in the picture below: